“Artificial intelligence is no longer just an idea in science fiction. It is a reality unfolding right now.”

Artificial intelligence is no longer just an idea in science fiction. It is a reality that is unfolding right now. In many developed countries, AI is already being used in a variety of work settings, changing the way tasks are completed. Even in everyday life, it’s closer than most people think; simply asking Siri a question on your phone is an example of interacting with an AI assistant. These technologies are becoming more capable, affecting industries in ways that would have seemed unlikely only a decade ago.
AI is transforming traditional careers, with some roles expected to disappear completely while others will change significantly. It is helping industries become more efficient and cost-effective, but it is also replacing certain human jobs at a pace never seen before. In this article, we explore 15 different jobs that may be taken over by AI in the future, looking at how each one could be affected and what that might mean for the people working in those fields.
1. Parking Enforcement

Parking enforcement might be one of those jobs we see vanish by the year 2050. Many car parks and garages are already making the switch to fully automated systems, using barriers, sensors, and advanced CCTV cameras. These systems can track licence plates, time your stay, and check if a car is parked legally without a human officer walking around with a ticket book. It’s becoming a smooth, efficient process that works around the clock.
In the future, this tech won’t just be in big city garages. It could be rolled out to smaller car parks and even side streets. That means traffic officers on patrol may no longer be needed, as cameras and software handle everything automatically. The change might feel strange at first, but for drivers, it could mean faster enforcement, fewer disputes, and less waiting around.
2. Customer Service
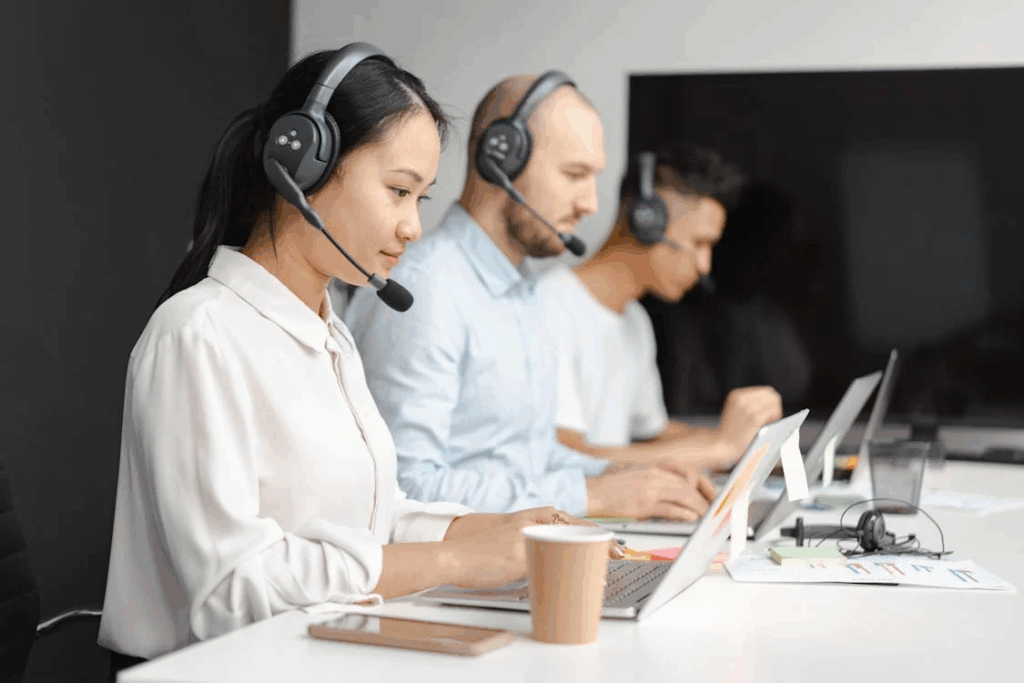

Customer service is already changing fast, and AI is playing a big part in it. More and more companies are letting chatbots and virtual assistants handle questions, complaints, and requests. These systems can “chat” just like a person and they keep improving through machine learning. That means they’re not only able to answer simple questions, but they can also deal with trickier problems that used to require a human representative.
Looking ahead, many customer service teams might rely heavily on AI chatbots, leaving fewer roles for human agents. Businesses like the idea because it’s faster, available 24/7, and often more cost-effective. For customers, it could mean getting instant help at any time of day, without waiting in a queue. Still, it’s a big shift, one that could make the job landscape look very different in just a few decades.
3. Cashier
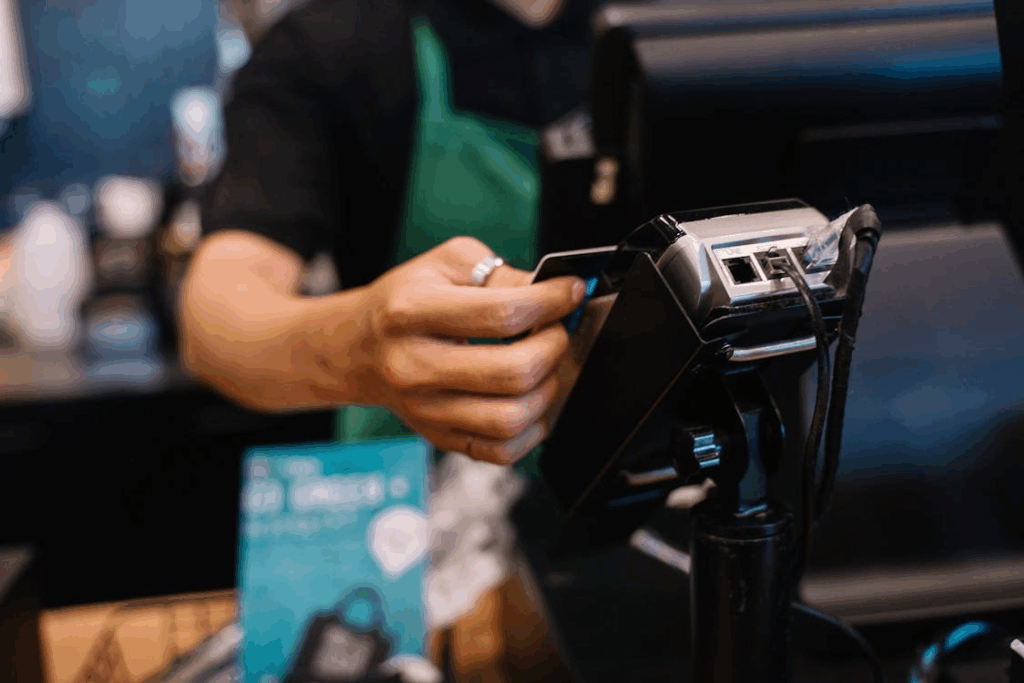

Cashier roles are already starting to disappear in some places, as big retailers experiment with completely automated shopping experiences. Companies like Amazon and Tesco are testing stores where you can simply walk in, pick up what you need, and leave. No checkout line in sight. In Central London, Tesco has even opened a store that works exactly this way, while some Uniqlo branches already let you pay using self-service machines.
These shops use advanced technology, combining cameras and sensors to track what you pick up and automatically charge you as you leave. It’s quick, efficient, and removes the need for a cashier behind the counter.
4. Truck and Taxi Drivers

Self-driving technology is advancing rapidly, with companies like Tesla and Waymo developing vehicles that can operate without human input. These systems are designed to navigate roads, follow traffic rules, and respond to changing conditions. In long-haul trucking, autonomous vehicles are seen as a way to handle the challenges of driver fatigue and extended travel times, while in taxis, they could manage routine trips without the need for a person at the wheel.
If these developments continue, a significant portion of trucking and taxi work could be carried out by autonomous vehicles in the future. Long-distance freight routes and common passenger journeys may be handled entirely by machines.
5. Financial Analyst
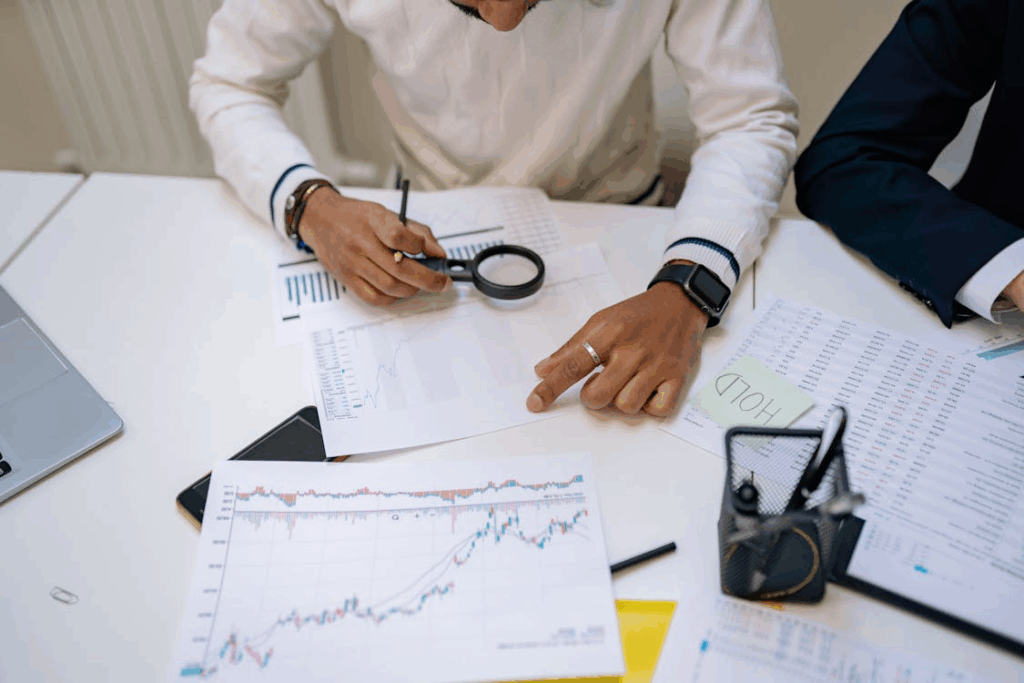

AI algorithms are becoming more capable in the world of finance, with the ability to process large amounts of data, forecast market movements, and generate investment suggestions. These systems can perform repetitive, rule-based tasks quickly and with a high degree of accuracy, making them useful tools for portfolio management and trading decisions. As the technology develops, many financial processes that once required extensive human analysis may be handled directly by AI systems.
This could lead to a reduced demand for human financial analysts in certain areas of the industry. While AI might take on much of the routine analysis, human roles could shift toward overseeing systems, interpreting results, or focusing on areas that still require personal judgment.
6. Proofreaders

AI tools such as Grammarly and other language-processing programs are becoming highly skilled at detecting spelling mistakes, grammar issues, and even style inconsistencies. These systems are trained on vast collections of text, allowing them to spot errors quickly and offer suggestions that can improve clarity and flow. Over time, they continue to refine their abilities, making them capable of handling a wide range of proofreading tasks that once required a careful human eye.
As these technologies advance, the demand for human proofreaders may decline in certain areas, especially for routine or high-volume work. However, some contexts may still rely on human expertise, particularly when tone, nuance, or specialised knowledge is involved. This shift highlights a broader change in how written content is reviewed and edited, with AI increasingly becoming a standard part of the process.
7. Data Entry
AI is increasingly able to automate the process of entering information into computer systems. Using advanced recognition technologies, it can extract data from forms, emails, and even scanned documents with speed and accuracy. This reduces the need for manual typing and checking, allowing large amounts of information to be processed in a shorter time.
As these systems become more widely used, the role of human data entry clerks may decline in many industries. Tasks that once required careful, repetitive input can now be completed automatically, with humans stepping in mainly for oversight or handling exceptions.
8. Translators and Interpreters

AI-based real-time translation has developed to the point where it can assist in both spoken and written communication almost instantly. Apps like Google Translate can use a microphone to listen to what someone is saying and translate it into the language you select. They can also take a photo of text, such as a sign, menu, or document, and provide a translation automatically. These features are already helping solo travellers manage in places where they don’t speak the local language.
As these tools continue to improve, they may influence how often human translators and interpreters are needed in everyday situations. While AI can offer quick and convenient translations, certain tasks, such as handling complex discussions, cultural nuances, or specialised topics, may still benefit from human expertise.
9. Delivery Drivers

Drones and AI-powered logistics systems are being tested in more places as a way to handle deliveries. Companies such as Amazon and UPS are investing in technology that can transport packages through the air, navigating directly to a customer’s address. These systems are designed to work quickly and efficiently, particularly for short-distance routes where speed is a priority.
If the technology continues to advance, it could take over many delivery tasks that are currently handled by human drivers. Short trips, small parcels, and time-sensitive orders may increasingly be managed by automated systems, while humans might focus on longer routes or more complex deliveries. This shift would bring changes to how goods are transported and the roles available within the delivery industry.
10. Receptionists

In places like hotels and corporate offices, automated check-in systems are becoming more common, taking on tasks that were once handled by receptionists. These systems can log visitors, schedule appointments, and provide answers to basic questions, often through touchscreens or AI-powered kiosks. Some locations are experimenting with more advanced solutions, such as humanoid robots, which can interact with guests in a way that feels more personal than a standard machine.
One example is the Henna Hotel in Tokyo, Japan, which uses robots as receptionists, bag checkers, and even concierges. As these technologies develop, they could become a regular part of front desk operations in different industries.
11. Graphic Designers

AI-enhanced design and editing tools are opening up new possibilities in how images and visuals are created. With just a single photo, these systems can generate highly realistic effects, such as showing what you might look like decades in the future or turning you into an anime-style character in minutes. Similar technology is already being used in producing creative content like music videos and short films for social media, showing how AI can quickly transform ideas into finished visuals.
As this technology advances, it may take on tasks that were once the responsibility of human graphic designers, particularly for quick or experimental projects. At the same time, designers may continue to play a role in shaping concepts, refining aesthetics, and ensuring that the final result aligns with a specific vision or brand.
12. Coders

AI tools like ChatGPT are now able to write fluent, syntactically correct code at a speed that often surpasses human capabilities. This means that tasks involving large volumes of basic or repetitive coding can be completed quickly by AI. For coders whose work mainly focuses on producing simple code in high quantities, this development could raise concerns about future job opportunities.
On the other hand, coders who focus on producing high-quality, well-structured software may find AI to be a helpful addition to their toolkit. By using AI to handle routine parts of the job, they can spend more time on complex problem-solving, creative solutions, and fine-tuning their projects.
13. Contractors

In April 2025, the CEO of Duolingo shared that the company would be taking an AI-first approach in the future. Part of this shift involves using AI in areas where contractors might have previously been hired, potentially changing how certain tasks are handled within the company. By integrating AI into these processes, some work that was once outsourced could be managed internally through automated systems.
Duolingo also announced plans to incorporate AI into their hiring process, joining the growing number of companies expected to use similar tools by the end of 2025. This move reflects a wider trend where AI is playing a larger role in recruitment, project management, and other operational areas.
14. Travel and Tourism

AI is becoming a useful tool in the travel and tourism industry, helping people plan trips and explore new destinations. AI assistants and chatbots can guide users through booking flights, renting vehicles, and finding accommodations, often tailoring suggestions to individual preferences. Some systems also perform flight forecasting, using historical price data to recommend the best times to book for cheaper fares. These tools can make trip planning more streamlined and accessible for a wide range of travellers.
For travel companies, AI offers ways to process and interpret the large amount of data generated by customers. It can compile feedback, reviews, and survey responses to assess performance and identify areas for improvement. This type of analysis can inform business strategies, marketing campaigns, and service enhancements.
15. Content Writers

Generative AI tools like ChatGPT and Gemini can create text that closely resembles human writing, producing articles, blog posts, and marketing copy in a short amount of time. This capability can be particularly impactful in areas where the writing does not require a high level of nuance, originality, or detailed research. As these systems become more widely used, certain types of content creation may be handled more by AI than by human writers.
At the same time, writing that is highly original, specialised, or deeply rooted in personal experience may become more valuable. As the internet fills with AI-generated material, genuine human perspectives could stand out as something unique. This shift may influence the kinds of writing opportunities available, with demand potentially moving toward work that AI struggles to replicate.
AI has the potential to make many processes faster, more efficient, and more accurate, changing the way tasks are handled across different industries. At the same time, human authenticity plays a vital role in maintaining creativity, empathy, and personal connection, qualities that machines cannot fully replicate. For individuals, learning AI-related technologies, automation tools, and the basics of machine learning can be a way to stay valuable in a workforce that is evolving alongside these advancements.
Rather than seeing AI solely as a replacement for human work, it can also be viewed as a tool to enhance industries. Businesses can use it to take over repetitive tasks, freeing people to focus on higher-value projects and problem-solving. By understanding AI’s role, adapting to its capabilities, and finding ways to collaborate with it, both individuals and organisations can position themselves to not only remain relevant but also grow in this new technological landscape.
Check out: How ChatGPT and AI Affect Education and The Best AI Prompts to Use for Your Studies